写可维护的代码
要有代码
有人也许为认为,代码不再是问题,我们正在临近代码的终结点,代码就会自动产生出来,不需要人工编写? 但事实是我们可以创造各种与需求接近的语言,可以创造帮助把需求解析和汇整为正式结构的各种工具,但是这些工具也需要代码的,语言也是需要翻译的,类似于java与javac(c++编写)的关系,所以代码永存。
要有可维护的代码
三个月编写,三年维护。 更多的时候程序是在被阅读,而不是在被编写 没有完工一说,修改程序的投入会远大于最初编写程序的投入 程序的阅读者需要理解程序-既从细节上,也从概念上。有时他们从细节开始,逐渐理解概念;有时他们从概念开始逐渐理解细节。
什么是可维护性高的代码
软件质量
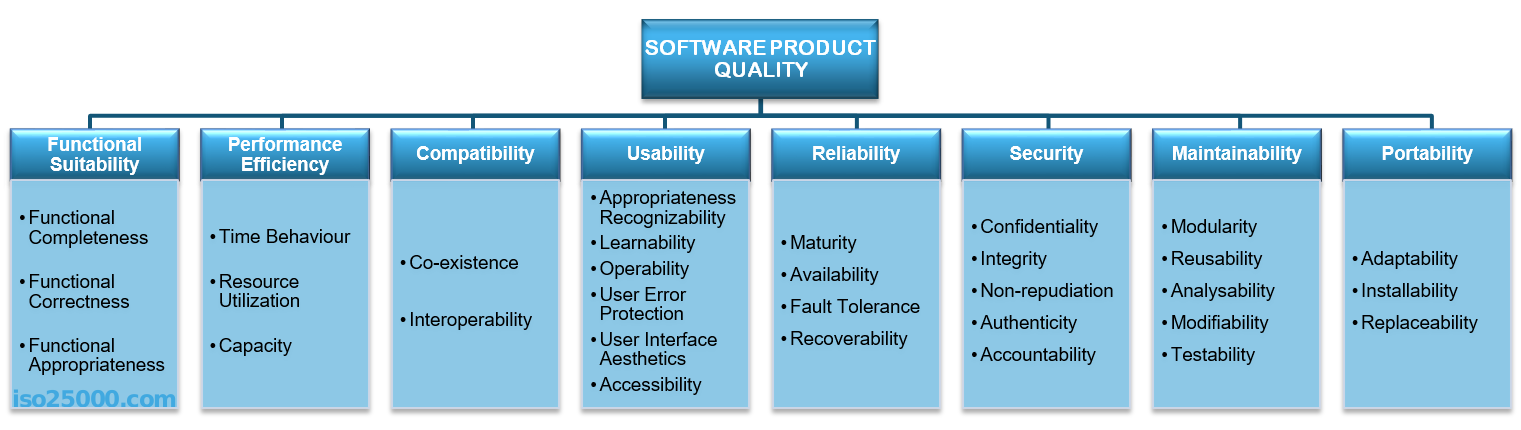
可维护性
| 子特性 | 定义 | 英文原版定义 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 可维护性 | 模块化 | 模块化的程度,模块间松耦合程度,改动一个模块对其他模块影响的程度。 | degree to which a system or computer program is composed of discrete components such that a change to one component has minimal impact on other components. |
| 可重用性 | 方法、类、模块等代码可以被复用的程度 | degree to which an asset can be used in more than one system, or in building other assets. | |
| 易分析性 | 评估系统打算改变其各个部分中的一个或多个的影响的成本和效率;诊断软件中的缺陷或失效原因的成本和效率;识别待修改部分成本和效率 | degree of effectiveness and efficiency with which it is possible to assess the impact on a product or system of an intended change to one or more of its parts, or to diagnose a product for deficiencies or causes of failures, or to identify parts to be modified. | |
| 可变性 | 系统可以被低成本高效率的修改,而不会引入缺陷和降低现有系统产品质量的程度 | degree to which a product or system can be effectively and efficiently modified without introducing defects or degrading existing product quality. | |
| 易测性 | 建立系统测试标准的成本和效率;测试可以运行来反映这些测试标准的程度 | degree of effectiveness and efficiency with which test criteria can be established for a system, product or component and tests can be performed to determine whether those criteria have been met. |
如何写可维护性高的代码
命名 提供不多不少、正确的信息
- 名副其实 用名字来讲述故事
-
rename method
未申请过退款是算退款成功呢,还是退款失败呢? isRefundMoneyOK -> isRefunding重构前
public Boolean isRefundMoneyOk(long userId, long tradeNo) { boolean isRefundMoneyOk = true; List<RefundRequestDO> refundRequestDOs = refundRequestMapperProxy .selectListByStatus(userId, tradeNo, null, null); if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(refundRequestDOs)) { isRefundMoneyOk = false; return isRefundMoneyOk; } for (RefundRequestDO refundRequestDO : refundRequestDOs) { if (RefundRequestDO.TypeEnum.REFUND.getCode() != refundRequestDO.getType() || RefundRequestDO.StatusEnum.AGREE.getCode() != refundRequestDO.getStatus() || RefundRequestDO.ResultEnum.SUCCESS.getCode() != refundRequestDO.getResult()) { isRefundMoneyOk = false; break; } } return isRefundMoneyOk; }重构后
public Boolean isRefunding(long userId, long tradeNo) { List<RefundRequestDO> refundRequestDOs = refundRequestMapperProxy .selectListByStatus(userId, tradeNo, null, null); if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(refundRequestDOs)) { return false; } for (RefundRequestDO refundRequestDO : refundRequestDOs) { if (RefundRequestDO.TypeEnum.REFUND.getCode() != refundRequestDO.getType() || RefundRequestDO.StatusEnum.AGREE.getCode() != refundRequestDO.getStatus() || RefundRequestDO.ResultEnum.SUCCESS.getCode() != refundRequestDO.getResult()) { return true; } } return false; }
-
- 精确,不说废话
- 语境信息 作用域、生命周期、类型都能用别的方式充分说明 OrderInfoMapper#selectOrderInfoByTradeNoFromMaster
- 揭示意图,而非实现, 除非实现策略对调用者有意义(跟我们一般使用抽象类型而不是具体类型的道理一样,面向接口编程)
- MedisLock.setNotExistKey VS Lock.lock
- CatUtil VS MonitorUtil
- select VS selectFromMaster (是否读主对调用方是有意义的)
- RiskControlRequestDeserializer#deserializeFieldsByBusinessLine()
- JDBC
- slf4j
- 类名和对象名 应该会是名词或者名词短语
- 方法名 应当是动词或者动词短语
注释
- 尽量不写注释 (类库,框架、API、TODO除外)
- 自描述:当觉得需要写注释才能表达清楚时,通常我会extract method
- 需要同步注释和代码的一致性 isRefunding
- TODO: 上线前清空TODO,上线后时机成熟后清理TODO
- 注释掉的代码 一律干掉
方法
用消息作为基本的控制流机制等于承认了变化是程序的基本状态(概念与细节)
原则
- 职责单一 风控和申请支付token变化率不一致 handleRiskControlAndPayment
-
局部化影响 封装变化,收敛变化。好处:1.可测试性高,待测的地方少 2.可变性高,更不易引入bug。 监控由jmonitor改为cat,并双写一段时间,是选择在所有打监控的地方添加cat的监控,还是在监控的方法内部添加cat的监控,对外调用方式不变? tradecenter监控有jmonitor改为cat
重构前
public CommonResponse<CreateOrderResponseBean> createOrder(CommonRequest<CreateOrderRequestBean> request) { CreateOrderRequestBean requestBean = request.getRequestData(); BusinessLineClientEnum businessLineClient = requestBean.getContextParam().getFillOrderInfo().getBuyInfo() .getBusinessLine(); MonitorUtil.monitor(businessLineClient, MonitorConsts.CREATE_ORDER); CatUtil.logMetricForCount(businessLineClient, CatConsts.CREATE_ORDER); ......下单代码 MonitorUtil.monitor(businessLineClient, MonitorConsts.CREATE_ORDER_SUCCESS); CatUtil.logMetricForCount(businessLineClient, CatConsts.CREATE_ORDER_SUCCESS); return CommonResponse.buildSuccess(createSuccessResponse(context.getCollectContext().getStandardParam().getOrderNo())); } public class MonitorUtil { private static final String SPLITTER = "_"; public static void monitor(BusinessLineClientEnum bizLine, String monitorKey) { JMonitor.add(bizLine.name() + SPLITTER + monitorKey); } } public class CatUtil { private static final String SPLITTER = "_"; private static final String ERROR_INFO_KEY = "errorInfo"; public static void logMetricForCount(BusinessLineClientEnum bizLine, String catKey) { Cat.logMetricForCount(bizLineName + SPLITTER + catKey); } }重构后
public CommonResponse<CreateOrderResponseBean> createOrder(CommonRequest<CreateOrderRequestBean> request) { CreateOrderRequestBean requestBean = request.getRequestData(); BusinessLineClientEnum businessLineClient = requestBean.getContextParam().getFillOrderInfo().getBuyInfo() .getBusinessLine(); MonitorUtil.monitor(businessLineClient, MonitorConsts.CREATE_ORDER); ......下单代码 MonitorUtil.monitor(businessLineClient, MonitorConsts.CREATE_ORDER_SUCCESS); return CommonResponse.buildSuccess(createSuccessResponse(context.getCollectContext().getStandardParam().getOrderNo())); } public class MonitorUtil { private static final String SPLITTER = "_"; public static void monitor(BusinessLineClientEnum bizLine, String monitorKey) { JMonitor.add(bizLine.name() + SPLITTER + monitorKey); Cat.logMetricForCount(bizLineName + SPLITTER + catKey); } } - 最小化重复 DRY
- extract method
- Replace Constructor with Factory Method
- method object
- 对称性、抽象层次一致
模式
- 消息 尽可能清晰和直接的表达逻辑,并且适当地推迟牵涉到的细节
- 分解性消息(助手方法)
spring的AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } } }
- 分解性消息(助手方法)
spring的AbstractApplicationContext#refresh
- 参数
- 参数越少越好、参数对象
- 可选参数
- 套筒型参数列表
- Remove Assignments to Parameters
- 临时变量
- 作用: 收集器、计数、解释、复用、元素
- 尽可能少的临时变量,重构的一大阻碍。 Replace Temp With Query
- 信息最小扩散原则 尽可能地缩短临时变量的垂直距离
- split temporary variable
- 卫语句 分清先决条件和主体逻辑,不需要用到复杂的控制结构,它的影响后果完全是局部的。
重构前
private void rollbackIfNeed(LogicResult executeResult, T context) { if (!executeResult.isSuccess()) { List<LogicUnit> reverseLogicList = executeResult.getInvocationInfo().getSuccessList(); if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(reverseLogicList)) { for (LogicUnit logicUnit : reverseLogicList) { try { LOGGER.warn("流程异常,逻辑rollback:{}", logicUnit.getClass().getSimpleName()); logicUnit.rollback(context, executeResult); } catch (Exception ex) { LOGGER.error("roll back for logic:{} fail, context:{}", logicUnit.getClass().getSimpleName(), context, ex); } } } } }重构后
private void rollbackIfNeed(LogicResult executeResult, T context) { if (executeResult.isSuccess()) { return; } List<LogicUnit> successList = executeResult.getInvocationInfo().getSuccessList(); if(CollectionUtils.isEmpty(successList)){ return; } for (LogicUnit logicUnit : successList) { try { LOGGER.warn("流程异常,逻辑rollback:{}", logicUnit.getClass().getSimpleName()); logicUnit.rollback(context, executeResult); } catch (Exception ex) { LOGGER.error("roll back for logic:{} fail, context:{}", logicUnit.getClass().getSimpleName(), context, ex); } } } - 异常
- 集合里的元素即使isNotEmpty,取出的数据元素也可能为null
- Replace Exception with Test
- UserInfoService#getUserInfoByUserId()
- Replace Error Code with Exception
- 同一进程内,不要用error code,跨进程可以使用error code
- null
- 不要返回null
- 抛异常(不要为调用方指定异常后的处理行为)通用服务层,基础设施层不要吃掉异常。
- 返回特例对象
- lamda表达式
类
原则
- 最小化重复
-
extract class
RiskControlRequestDeserializer ``` public class RiskControlRequestDeserializer {private static final Map<BusinessLineClientEnum, Class<? extends BaseRiskControlRequest» RISK_CONTROL_REQUEST_CLASS_MAP = ImmutableMap.<BusinessLineClientEnum, Class<? extends BaseRiskControlRequest»builder() .put(BusinessLineClientEnum.menpiao, TicketRiskControlRequest.class) .put(BusinessLineClientEnum.gentuanyou, TravelRiskControlRequest.class) .put(BusinessLineClientEnum.jiujing, JingJiuRiskControlRequest.class) .put(BusinessLineClientEnum.flightx, FlightxRiskControlRequest.class) .build();
public static BaseRiskControlRequest deserializeFieldsByBusinessLine(String riskParamJson, BusinessLineClientEnum bizLine) { Class<? extends BaseRiskControlRequest> riskControlRequestClass = RISK_CONTROL_REQUEST_CLASS_MAP.get(bizLine); return JsonUtils.json2Object(riskParamJson, riskControlRequestClass); }
} ```
-
- 逻辑与数据捆绑变化率(数据、逻辑)
InputWebContextParam
public class InputWebContextParam { /** * 参数可能是mt i版 或者 native */ private InputCommonParam commonParam; /** * 买家的客户端信息 */ private InputClientInfo clientInfo; /** * 账号体系信息 */ private InputUserInfo userInfo; /** * 渠道信息 */ private InputChannelInfo channelInfo; /** * 产品信息 */ private InputProductInfo productInfo; /** * 订单内容 */ private InputFillOrderInfo fillOrderInfo; /** * 资金信息 */ private InputPayInfo payPoolInfo; /** * 扩展信息 */ private InputExtensionalInfo extensionalInfo; } - 信息最小扩散
类间
原则
- 单一职责原则 S
- 开闭 O
- 里式替换 L
- 接口隔离 I logic reversible
- 依赖倒置 D 标准化都是这个设计原则的体现 中台定义接口标准
- 合成复用(多用组合,少用继承) 继承-实现-聚合-组合-关联-依赖
- 迪米特法则(最少知识原则) tradecenter的结构, 保险的版本号获取,wrapper methods
- 好莱坞法则 控制权的收敛转移 spring IOC 模板方法 规则容器
设计模式
- 工厂 多是简单工厂
- 代理 事务、数据双写、数据应用、热点数据读主
- 策略
- 支付回调处理
private static PayNotifyStrategy.Strategy findPayNotifyStrategy(String callbackOutNo, OrderInfoDO orderInfoDO) { PayLogMapper payLogMapper = SpringBeanUtil.getBean(PayLogMapper.class); PayLogDO payLogDO = payLogMapper .selectPayLogByTradeNoAndStatusFromMaster(orderInfoDO.getTradeNo(), PayLogStatusEnum.PAY_OK.getCode()); LOGGER.info("支付回调查找策略findPayNotifyStrategy:callbackOutNo:{},orderInfo:{},paylogDo:{}", callbackOutNo, orderInfoDO, payLogDO); if (payLogDO != null) { if (callbackOutNo.equalsIgnoreCase(payLogDO.getOutNo())) { return PayNotifyStrategy.Strategy.SamePay; } else { return PayNotifyStrategy.Strategy.TwicePay; } } // 暂时只关注跟团游 // 1:待支付 ,8:支付成功, 32:取消(退完), 64:关闭 if (orderInfoDO.getStatus() == 1 || orderInfoDO.getStatus() == OrderDBState.PAY_WAIT.getCode()) { return PayNotifyStrategy.Strategy.FirstPaySuccess; } if (orderInfoDO.getStatus() == 64) { return PayNotifyStrategy.Strategy.PayTimeout; } return null; } - 游玩人联系人规则转换
- 支付回调处理
- 享元 ThriftPayConfirmTool
public class ThriftPayConfirmTool { private static Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ThriftPayConfirmTool.class); private static Map<String, ThriftPayConfirm2BusinessService> SERVICE_CACHE = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(); public static BooleanResponse notifyPayConfirm(PayConfirmNotice2BusinessRequest request, MtClientProxyBuilder.APIInfo apiInfo) { String appKey = apiInfo.getRemoteAppKey(); ThriftPayConfirm2BusinessService service = SERVICE_CACHE.get(appKey); try { if (service == null) { synchronized (ThriftPayConfirmTool.class) { ThriftPayConfirm2BusinessService newService = (ThriftPayConfirm2BusinessService) MtClientProxyBuilder .createInstance(apiInfo); SERVICE_CACHE.put(appKey, newService); service = newService; } } } catch (Exception e) { LOGGER.error("初始化Thrift失败:", e); } BooleanResponse notifyBizResult = service.notify4PayConfirm(request); return notifyBizResult; } } - 观察者 事件驱动
- 模板 执行框架、保险plus多种任务执行
public LogicResult doLogicSchedule(T context, LogicGroup<T> group) { List<LogicUnit<T>> allLogic = group.getAllLogic(); LogicResult.InvocationInfo invocationInfo = buildInvocationInfo(); LogicResult logicResult = null; for (LogicUnit logicUnit : allLogic) { if (!mapping(context, logicUnit)) { continue; } try { invocationInfo.setLast(logicUnit); logicResult = logicUnit.doLogic(context); } catch (Exception ex) { logicResult = LogicResult.createException(ex); } if (!logicResult.isSuccess()) { invocationInfo.getFailList().add(logicUnit); LifecycleLogger.error(logicUnit + "执行失败, context" + context + ", 原因:" + logicResult.getMessage()); break; } else { invocationInfo.getSuccessList().add(logicUnit); LifecycleLogger.info(logicUnit + "执行成功"); } } logicResult.setInvocationInfo(invocationInfo); rollbackIfNeed(logicResult, context); return logicResult; } -
组合 order的数据推送 ``` public abstract class CompositeLogic implements Logic {
protected List
childLogicList = Lists.newArrayList(); @PostConstruct protected void init() { registerAllLogic(); }
protected abstract void registerAllLogic();
protected void registerLogic(Class<? extends Logic> clazz) { childLogicList.add(SpringBeanUtil.getBean(clazz)); }
@Override public boolean async() { return false; }
@Override public void doLogic(DataPushContext context) { for (Logic logic : childLogicList) { if (logic.async()) { AsyncTool.submit(() -> { logic.doLogic(context); }); } else { logic.doLogic(context); } } } }
public class MtpCompositeLogic extends CompositeLogic {
@Override
protected void registerAllLogic() {
registerLogic(InsuranceLogicUnit.class);
registerLogic(PersistenceCompositeLogic.class);
registerLogic(ACKSuccessLogicUnit.class);
registerLogic(CloseOrderLogicUnit.class);
registerLogic(OperationLogLogicUnit.class);
registerLogic(CreatedEventLogicUnit.class);
registerLogic(HiveLogLogic.class);
} }
public class PersistenceCompositeLogic extends CompositeLogic {
@Override
protected void registerAllLogic() {
registerLogic(UserIdMapPersistenceLogicUnit.class);
registerLogic(OrderExtendsPersistenceLogicUnit.class);
registerLogic(OrderMultiLevelPersistenceLogicUnit.class);
registerLogic(ContactPersistenceLogicUnit.class);
registerLogic(VisitorsPersistenceLogicUnit.class);
registerLogic(BookInfoPersistenceLogicUnit.class);
registerLogic(OrderUserRelationPersistenceLogicUnit.class);
registerLogic(BookGoodInfoPersistenceLogicUnit.class);
registerLogic(InsurancePersistenceLogicUnit.class);
registerLogic(MtpNotifyStatusManagePersistenceLogicUnit.class);
}
@Override
@Transactional
public void doLogic(DataPushContext context) {
super.doLogic(context);
} } ``` * 门面 用户界面层和应用层的解耦 (门票的徒有其表)
IDEA重构快捷键
| 快捷键 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| OPT + ENTER | 显示意图动作和快速修复 |
| CTRL + OPT + H | 查找方法调用mark |
| SHIFT + F6 | 重命名 |
| CMD + OPT + M | 修改方法签名 |
| CMD + OPT + V | 提取方法 |
| CMD + OPT + C | 提取常量 |
消除一切可消除的黄色!!!
模块/系统
原则
- 围绕业务概念建模
- 接受自动化文化
- 隐藏内部实现细节
- 让一切都去中心化
- 可独立部署
- 隔离失败
- 高度可观察
建模
- 共享模型
- 模型存在内部和外部两种表示形式
- 同一个名字在不同的限界上下文有着完全不同的含义,术语只有在限界上下文内才有意义
- 微服务应该清晰的和限界上下文保持一致,服务边界应和领域的限界上下文保持一致
集成
- 客户端库
- 禁止数据库集成
- 版本管理(http、rpc)
- 尽可能延迟
- 语义化的版本管理
- 用户界面
分层
现有order分层
* api层
* biz层
* service层
* dao层
阿里巴巴开发手册分层
领域驱动设计分层
模型穿透问题
参考
实现模式
重构
代码整洁之道