Collection常用子类源码注解
类图
List和set的
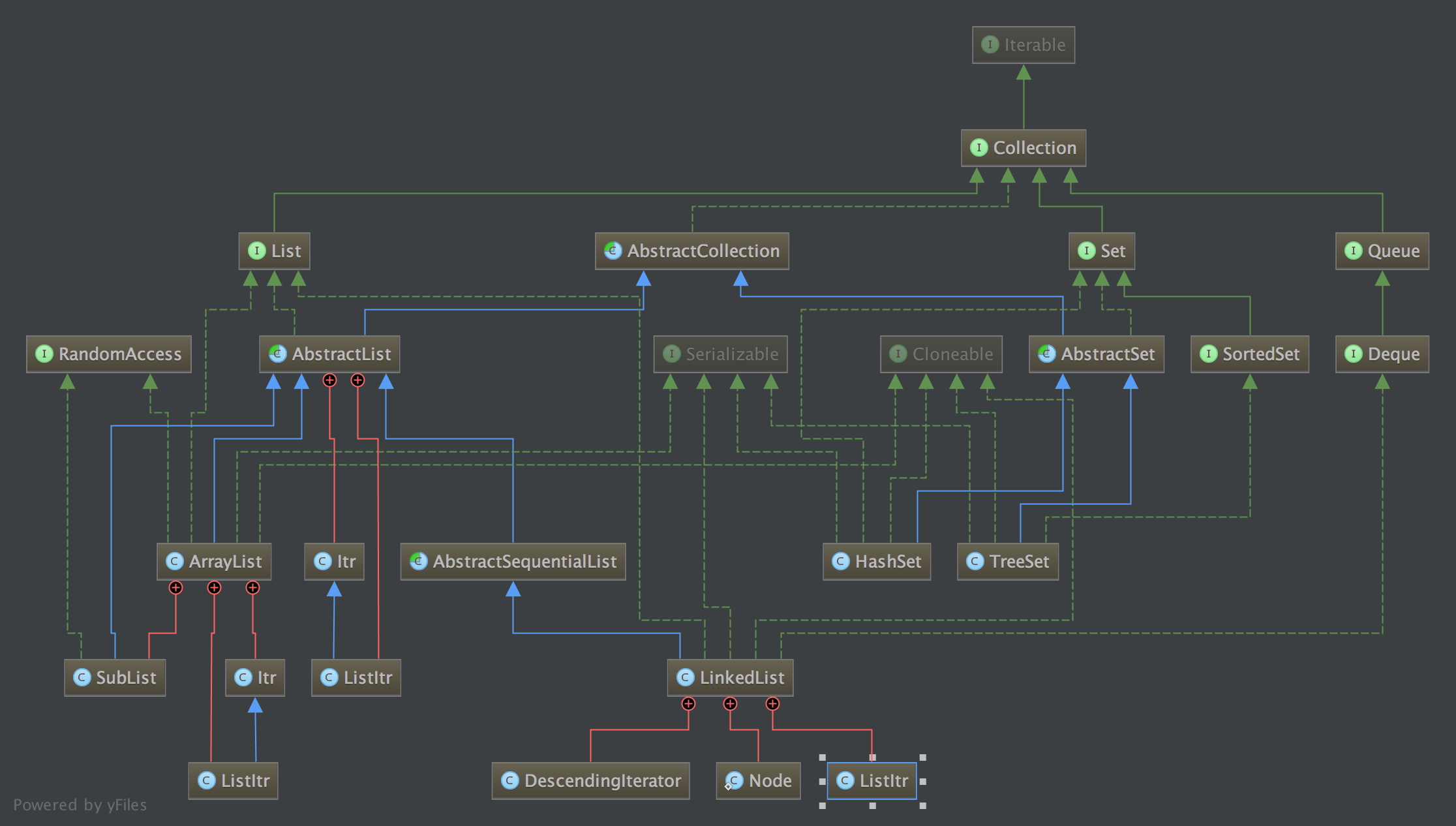
公共部分
Iterable
Iterable 只有一个接口返回一组元素的迭代器,实现该接口的类都支持foreach语句
Collection
- add(E) 添加一个元素,返回集合是否变更
- addAll(Collection<? extends E>) 添加一组元素
- clear() 清空集合
- contains(Object) 是否包含元素
- equals(Object) 各子类重写Object的equals方法.例如ArrayList的是:
两个list各个位置的元素是否完全相同 - hashCode() 重写了equals方法就要重写hashCode
- isEmpty() 是否为空
- iterator() 返回迭代器
- remove(Object) 删除元素
- removeAll(Collection<?>) 删除一组元素
- retainAll(Collection<?>) 过滤一组元素
- size()集合大小
- toArray() 返回对象数组
- toArray(T[] a) 返回T类型的数组,这里指明了对象类型
AbstractCollection
其中AbstractCollection对Collection的部分方法进行了实现(除了iterator()和size()),包含了一些List和Set共有的操作
/**
* @param src the source array. ***源数组***
* @param srcPos starting position in the source array. ***源数组起始地址***
* @param dest the destination array. ***目标数组***
* @param destPos starting position in the destination data. ***目标数组开始的地址***
* @param length the number of array elements to be copied. ***要拷贝的长度***
* @exception IndexOutOfBoundsException if copying would cause
* access of data outside array bounds. ***length不能超过src和dest的任一长度***
* @exception ArrayStoreException if an element in the <code>src</code>
* array could not be stored into the <code>dest</code> array
* because of a type mismatch. ***类型不匹配***
* @exception NullPointerException if either <code>src</code> or
* <code>dest</code> is <code>null</code>. ***src或者dest为空***
*/
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos,
Object dest, int destPos,
int length);
List
List接口在Collection的基础之上增加了部分list独有的操作
- add(int,E) 在list某位置处添加元素
- addAll(int,Collection<? extends E>)在list某位置处添加元素组
- get(int) 根据下标获取元素
- indexOf(Object) 根据元素获取下标,如果多个返回第一个
- lastIndexOf(Object) 根据元素获取最后一个的下标
- listIterator() 返回list的迭代器
- listIterator(int) 从list某下标处返回迭代器
- remove(int) 删除下标某处的元素,返回删除的元素
- set(int,E) 设置list某处的元素
- subList(int,int) 返回下标1和下标2之间的list
AbstractList
AbstractList对List接口进行了实现,并引入了SubList,Itr和ListItr三个内部类,用于实现subList和listIterator方法,并增加了一个域modCountstructurally modified的次数(transient修饰)
ArrayList
ArrayList的elementData,存储list元素的数组,并且这个域是transient(不参与序列化)修饰的,因为ArrayList重写了readObject和writeObject
ArrayList在AbstractList之外多了一些方法
- clone() 重写了Object#clone()方法, 除了clone list对象本身,还clone list的每个元素
- ensureCapacity(int) 增加ArrayList实例的容量(确保能保存最小的容量)
- trimToSize() 将list的容量trim到list当前的size
Queue
- add(E) 在队列中添加特定的元素,成功则返回true,如果没有多余空间则抛出IllegalStateException
- element() 返回队首元素,它和peek()方法的不同是,如果队列为空,element()抛出noSuchElementException,peek()返回null
- offer(E) 类add()方法,When using a capacity-restricted queue, this method is generally preferable to {@link #add}, which can fail to insert an element only by throwing an exception.
- peek() 返回队首元素,如果队列为空,返回null
- poll() 返回队首元素,并从队首移除,如果队列为空,返回null
- remove() 返回队首元素,并从队首移除,如果队列为空,抛出noSuchElementException
Deque
- addFirst(E) 在对头添加元素,无返回值
- addLast(E) 在队尾添加元素,无返回值
- descendingIterator() 返回插入顺序相反的iterator
- getFirst() 获取对头元素,和peekFirst()不同的是如果队列为空,getFirst()抛出noSuchElementException异常,peekFirst()返回空
- getLast() 类getFirst()
- offerFirst(E) 在对头添加元素,返回添加的元素
- offerLast(E) 在对头添加元素,返回添加的元素
- peekFirst() 获取队首元素,如果队列为空,返回null
- peekLast() 获取队尾元素,如果队列为空,返回null
- pollFirst() 返回队首元素,并从队列移除,如果队列为空,返回null
- pollLast() 返回队尾元素,并从队列移除,如果队列为空,返回null
- pop() 返回队首元素,并从队列移除,方法等价于removeFirst(),如果对列为空,抛出NoSuchElementException
- push() 等价于addFirst()
- removeFirst() 见pop()
- removeFirstOccurrence(Object) 移除对象在队列中的首次出现,如果移除成功,返回true,
- removeLast() 返回队尾元素,并从队列移除,如果对列为空,抛出NoSuchElementException
- removeLastOccurrence() 移除对象在队列中的最后次出现,如果移除成功,返回true,
LinkedList
LinkedList是基于双向循环链表来实现的,数据结构如下:
类声明,LinkedList只是把所实现的接口统统实现了下
public class LinkedList<E> extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
双向链表的结构体
private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
Set
set 接口和collection接口方法完全一样
AbstractSet
- 重写了equals(Object o)方法,集合A和B size相等,并且A包含B所有元素
- 重写了hashCode() 重写了equals方法就要重写hashCode方法
- 实现了removeAll(Collection<?> c)
SortedSet
- Comparator<? super E> comparator() 返回这个sortedSet的比较器
- E first() 返回这个Set的第一个元素
- E last() 返回这个Set的最后一个元素
- SortedSet
headSet(E toElement) 返回这个set小于toElement的set - SortedSet
tailSet(E fromElement) 返回这个set大于fromElement的set - SortedSet
subSet(E fromElement, E toElement) 返回这个set从fromElement(包括)到toElement(不包括)的set
NavigableSet
- E lower(E e) 返回集合中小于元素e的最大的元素
- E floor(E e) 返回集合中小于或等于元素e的最大的元素
- E ceiling(E e) 返回集合中大于或等于元素e的最大的元素
- E higher(E e) 返回集合中大于元素e的最大的元素
- E pollFirst() 类似(#Deque)的,返回集合的最小元素,并从集合中移除
- E pollLast() 类似(#Deque)的,返回集合的最大元素,并从集合中移除
- Iterator
iterator() .. - NavigableSet
descendingSet() 返回逆序的set - Iterator
descendingIterator() 返回逆序的iterator - NavigableSet
subSet(E fromElement, boolean fromInclusive, E toElement, boolean toInclusive) ... - NavigableSet
headSet(E toElement, boolean inclusive) ... - NavigableSet
tailSet(E fromElement, boolean inclusive) ... - SortedSet
subSet(E fromElement, E toElement) == subSet(fromElement, true, toElement, false) - SortedSet
headSet(E toElement) == headSet(toElement, false) - SortedSet
tailSet(E fromElement) == tailSet(fromElement, true)
TreeSet
HashSet
- 实际上是通过HashMap来实现的
map.put(e, PRESENT)==null; - 不保证集合元素的顺序
- 允许空值
- Set s = Collections.synchronizedSet(new HashSet(…))
- 其迭代器是fail-fast的,迭代器一旦创建,除了迭代器自己删除元素,
其他任何的对set的写操作都会导致迭代器抛出
ConcurrentModificationException, 注意迭代器的fail-fast特性不能保证,正如在非同步化修改中做保也是不可能的. 因此通过异常来判定程序的正确性是不可取的,只能把它当做检测程序bug的手段