文件系统
下载linux源码 sudo apt-get install linux-source //代码将被下载到/usr/src/下,我的是3.13.0
主要涉及这四个数据结构inode,file,dentry,superblock
inode
代码位置:include/linux/fs.h#inode(ps:源码太长,下是大致结构)
/* Metadata returned by the stat and fstat functions */
struct stat{
dev_t st_dev; /* Device */
ino_t st_ino; /* inode */
mode_t st_mode; /* Protection and file type */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* Number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* User ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* Group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* Device type (if inode device) */
off_t st_size; /* Total size, in bytes */
unsigned long st_blksize; /* Blocksize for filesystem I/O */
unsigned long st_blocks; /* Number of blocks allocated */
time_t st_atime; /* Time of last access */
time_t st_mtime; /* Time of last modification */
time_t st_ctime; /* Time of last change */
};
上图中stat的信息就保存在这个数据结构中,文件的FileMetadata(元信息,inode,vnode)
设备:801h/2049d 设备信息
Inode:6029317 inode号
权限:(0664/-rw-rw-r--) 文件类型及权限
硬链接:1 硬链接的个数
Uid:( 1000/ lcj)
Gid:( 1000/ lcj)
普通文件 设备类型//todo?
大小:2 文件大小
IO块: IO块数(block数)
块:8 块数(扇区数)
最近访问:2015-12-17 22:17:01.927402539 +0800
最近更改:2015-12-17 22:17:01.927402539 +0800
最近改动:2015-12-17 22:17:01.927402539 +0800
file
代码位置:include/linux/fs.h#file
struct file {
union {
struct llist_node fu_llist;
struct rcu_head fu_rcuhead;
} f_u;
struct path f_path;
#define f_dentry f_path.dentry
struct inode *f_inode; /* cached value */
const struct file_operations *f_op;
/*
* Protects f_ep_links, f_flags, f_pos vs i_size in lseek SEEK_CUR.
* Must not be taken from IRQ context.
*/
spinlock_t f_lock;
atomic_long_t f_count;
unsigned int f_flags;
fmode_t f_mode;
loff_t f_pos;
struct fown_struct f_owner;
const struct cred *f_cred;
struct file_ra_state f_ra;
u64 f_version;
/* needed for tty driver, and maybe others */
void *private_data;
};
dentry
代码位置: include/linux/dcache.h#dentry
struct dentry {
/* RCU lookup touched fields */
unsigned int d_flags; /* protected by d_lock */
seqcount_t d_seq; /* per dentry seqlock */
struct hlist_bl_node d_hash; /* lookup hash list */
struct dentry *d_parent; /* parent directory */
struct qstr d_name;
struct inode *d_inode; /* Where the name belongs to - NULL is
* negative */
unsigned char d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN]; /* small names */
/* Ref lookup also touches following */
struct lockref d_lockref; /* per-dentry lock and refcount */
const struct dentry_operations *d_op;
struct super_block *d_sb; /* The root of the dentry tree */
unsigned long d_time; /* used by d_revalidate */
void *d_fsdata; /* fs-specific data */
struct list_head d_lru; /* LRU list */
struct list_head d_child; /* child of parent list */
struct list_head d_subdirs; /* our children */
/*
* d_alias and d_rcu can share memory
*/
union {
struct hlist_node d_alias; /* inode alias list */
struct rcu_head d_rcu;
} d_u;
};
super_block
代码位置:include/linux/fs.h#super_block
linux如何表示打开的文件
内核的三个数据结构
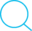
描述符表每个进程都有它独立的描述符表 ,它的表项是由进程打开的文件的描述符,每个打开的描述符表项指向文件表中的一个表项. 一个进程可以打开多少个文件 具体配置在这/etc/security/limits.conf(centos) 可以通过ulimit -n来查看打开文件表所有的进程共享这张表,打开文件的集合是由一张文件表来表示,inode表(stats,inodes)所有的进程共享这张表,每个表项包含stat结构的大多信息.
不同的文件打开方式
- 打开不同的文件
不同的文件被打开之后,得到不同的文件描述符,放在这个进程描述符表中。在文件表中,也会有不同的文件表项,这个表项记录有当前的文件位置,引用计数和一个指向 inode表中对应表项的指针。这样,不同的文件被打开,对应进程描述符表中的不同描述符,然后对应所有进程中的文件表,文件表中又对应着不同的inode表项
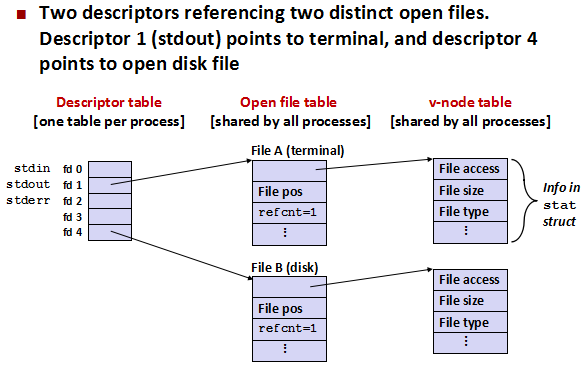
- 同一个文件被打开多次
同一个文件被打开多次之后,产生多个文件描述符,对应文件表中的多个表项,而这些表项中的记录却指向同一个inode表项
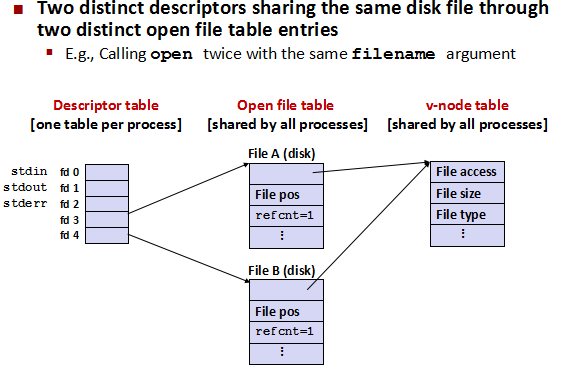
- 子进程共享文件
在fork之后,子进程复制了父进程的描述符表(每个进程一个),如果父进程已经有打开的 文件,子进程就会继承下来,父子进程就拥有共同的文件表项,所以inode表项相同 每个inode保存了文件系统中的一个文件系统对象(包括文件、目录、设备文件、socket、管道, 等等)的元信息数据,但不包括数据内容或者文件名。 文件系统创建(格式化)时,就把存储区域分为两大连续的存储区域。
逻辑到物理
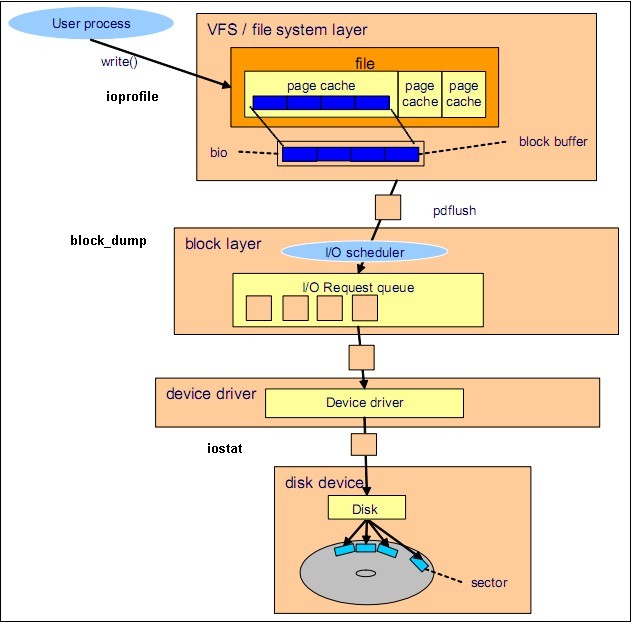
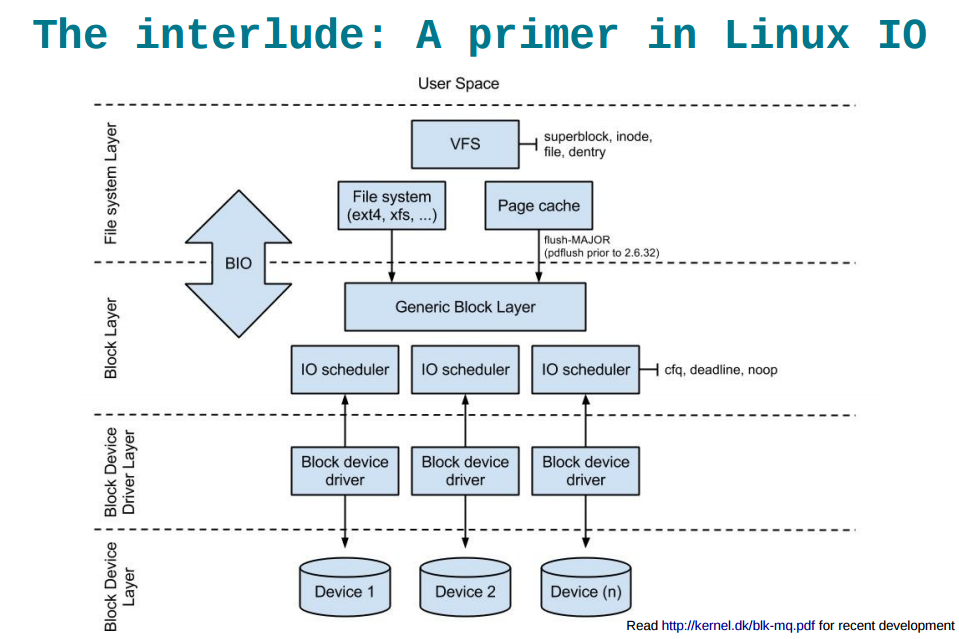
总: 文件描述符表->打开文件表->inode表->对应的逻辑块号->对应的物理块号
[1]http://www.xuebuyuan.com/1239921.html
[2]https://ext4.wiki.kernel.org/index.php/Ext4_Disk_Layout
[3]http://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/academic/class/15213-f15/www/schedule.html