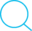
一些速度
一些速度
| 硬件 | 速度 |
|---|---|
| L1 cache reference 读取cpu的一级缓存 | 0.5ns |
| Branch mispredict 转移,分支预测 | 5ns |
| L2 cache reference 读取cpu的二级缓存 | 7ns (14 × L1cache) |
| Mutex lock/unlock 互斥锁/解锁 | 25ns |
| Main memory reference 读取内存数据 | 100ns (20 × L2 cache,200 × L1 cache) |
| Compress 1k bytes with zippy 1k字节压缩 | 3000ns |
| Send 1k bytes over 1 Gbps network 在1Gbps的网络上发送1k字节ps: 1Gbps (带宽) 一秒发送1Gbits(不是bytes) | 10,000ns 0.01ms |
| Read 4k randomly from SSD | 150,000ns 0.15ms |
| Read 1MB sequentially from memory 从内存顺序读取1MB | 250,000ns 0.25ms |
| Round trip within same datacenter 从一个数据中心往返一次,ping 一下 | 500,000ns |
| Disk seek 磁盘搜索 | 10,000,000ns 20 x datacenter roundtrip |
| Read 1MB sequentially from network 从网络上顺序读取1兆数据 | 10,000,000ns |
| Read 1MB sequentially from disk 从磁盘读取1兆 | 30,000,000ns |
| Send packet CA ->Netherlands -> CA 一个包的一次远程访问 | 150,000,000ns |
根据上述,算一下一秒读取的字节数
- 1Gbps的带宽 128M
- 内存中顺序读取 4G
- 从ssd中随机读取 27M 顺序读取 200+M
- 从网络顺序读取 100M
- 从磁盘顺序读取 33M
相关术语
-
qps 每秒查询数qps 在很大程度上代表系统在业务上的繁忙程度,而每次的请求的背后,可能对应着多次磁盘I/O,多次网络请求,以及多个CPU时间片,通过关注系统的qps数,我们能够非常直观的了解到当前系统业务情况。
-
rt response time 请求的响应时间。通过部署cdn边缘节点来缩短用户请求的物理路径,通过内容压缩来减少传输的字节数,使用缓存来减少磁盘I/O和网络请求等。
-
cdn 内容分发网络
-
tps 每秒事务数
-
pv page view
-
uv unique vistor
-
tp50,tp90,tp99:
tp90 = top percentile 90 Imagine you have response times:10s,1000s,100s,2s Calculating TP is very simple:
- Sort all times in ascending order: [2s, 10s, 100s,1000s]
- find latest item in portion you need to calculate.
2.1 For TP50 it will be ceil(4*0.5) = 2 requests. You need 2nd request.
2.2 For TP90 it will be ceil(4*0.9) = 4. You need 4th request.
- We get time for the item found above. TP50=10s. TP90=1000s